What Does P Mean On A Camera
Video jargon explained: what the specs hateful and what to look for

Every new video camera comes with a baffling list of bullet points, specifications and features to explicate why it's amend than anything else that'south gone before, but what do they all hateful, and how important are they actually?
Many of the things you look for in a stills camera are important for video besides, notably things like sensor size and ISO range. But video capture introduces a whole range of other aspects and technicalities beyond this, and so here'due south a guide to some of the jargon y'all're probable to come across, and what it means in real terms.
• Encounter the Digital Photographic camera Earth A-Z Lexicon of photography jargon
• See also: Best VHS to DVD converters
Video resolution

12K, 8K, 6K, C4K, 4K UHD, FHD, Hard disk… in that location are so many different resolutions now! HD is the sometime 'standard Hard disk' with a frame width of 1280 pixels, while FHD is 'FullHD' with the larger and more widely used 1920 pixel width. After that, the number indicates the approximate frame width in pixels, so 4K is video iv,000 pixels wide, 6K is video 6,000 pixels broad and and then on. Despite the headline stories about 6K, 8K and beyond, 4K is the most universal electric current resolution and still very high for most purposes.
4K vs Picture palace 4K (C4K)
What virtually people refer to as '4K' is actually UltraHD, or 3840x2160 pixels; information technology's non quite 4,000 pixels (or 4K) pixels wide. However, information technology does have the same 16:9 aspect ratio as FullHD, with twice the horizontal and vertical resolution. Actual Movie theater 4K, which is frequently referred to as DCI 4K, has a resolution of 4096x2160 pixels, with a slightly wider 17:ix aspect ratio.
8K
Encounter What is 8K?
Aspect ratios
Aspect ratio is the video frame's width versus its acme. It's particularly important for video, where y'all want the video proportions to match the screen or display it'due south being shown on. By far the most common aspect ratio is xvi:nine (16 units broad by 9 high). This is used past almost all common video modes on cameras, by domestic Tv sets and calculator monitors. In that location are wider ratios than this and used in cinema productions. Cinema 4K (C4K or DCI 4K) has a slightly wider aspect ratio than regular 4K UHD and is offered on some cameras, and there are much wider cinematic ratios than this that are simply used in the movie industry.

Anamorphic lens
This is a special kind of lens used widely when movies were shot on fixed film sizes, to squash a wide prototype horizontally to fit on a narrower film area. Another anamorphic lens would be used to project or otherwise display the movie and stretch information technology back out to its proper proportions. Anamorphic lenses are starting to make a comeback in digital video as they offering a way to capture much wider scenes than would otherwise fit on the camera sensor. They also produce optical effects, such equally eliptical bokeh shapes, and streaky flare that many cinematographers love.
Autofocus
Virtually camera makers now offer fast hybrid phase- and contrast-detection autofocus systems, though Nikon DSLRs all the same use dissimilarity-detect autofocus in live view and during video recording, and Panasonic'southward Depth From Defocus (DFD) contrast-discover AF is really fast. In reality, though, many videographers adopt transmission focus.
Crops and sensor sizes
Sensor size is as important for video equally it is for stills photography because larger sensors produce ameliorate quality, especially in depression light, and give shallower depth of field for a more 'cinematic' effect. But a camera may not always be able to use the total width of the sensor when shooting video, depending on the sensor resolution, the frame rate existence used and the camera's processing capabilities. Some full frame cameras, for case, can only shoot 'cropped' video using a smaller, central surface area of the sensor. There is a general move towards full frame sensors in video, where previously the standard was the Super 35 format (roughly APS-C size) which remains in widespread use and is oft provided on total frame cameras as a 'crop' way for the reasons explained in a higher place.

Pixel binning vs oversampling
Some video cameras are fabricated with sensors that have exactly the same resolution in pixels equally the video they capture. With cameras that shoot both stills and video, however, the sensor resolution volition often be a lot higher than is needed for video – yous only need a 12MP sensor to capture 4K, for example. This leaves manufacturers with 3 choices:
1) Capture cropped video using a smaller surface area of the sensor with the same pixel dimensions equally the video – this needs least processing only reduces the angle of view of your lenses.
2) Use 'pixel binning' or 'line skipping' to combine or discard unwanted pixels – this is mostly seen as a rather unsatisfactory, low tech approach.
iii) Use 'oversampling' to capture video frames at the sensor's full resolution and and then resample them on the fly downwardly to the required video resolution – this is regarded as giving the all-time quality and does not crop the video frame, but does require more than processing power.
Interlaced versus progressive
In the sometime days of broadcast TV, when signal bandwidth was limited, interlacing was used to transmit video frames in two parts, one with odd lines and one with even lines only, then 'interlace' them on the TV screen. Information technology worked well plenty, but you tin easily come across the interlacing in freeze-frames or digitised one-time Television set programs. In the early days of digital video, many cameras still used interlacing to brand the best of the limited processing power available at the time. Now, though, almost all video is 'progressive', where each video frame is captured in full. The quality is much better and you no longer become the horrible striped interlacing issue. When you see a 'p' afterward a video format, eastward.grand. 1080p, or a frame rate of 30p, information technology means progressive capture, whereas 'i' ways interlaced capture.

Frame rates
For video to look smooth it needs a recording and playback speed of 24-30fps. 24fps is popular in cinematography, 25fps is used for broadcast Tv set and playback devices in the UK and many European territories and part of the old PAL standard, and 30fps in the The states and other territories every bit in the old NTSC standard. Videographers will often choose the frame rate to lucifer the territory they are in, though with digital distribution and playback, the differences are becoming less important, equally are the differences between the PAL and NTSC systems. Cameras offer multiples of these frame rates for slow movement effects. 60fps recording and 30fps playback will give a 2x wearisome motility issue, for example. Loftier frame rates are a selling bespeak for video cameras only are processor intensive and may come with lower video resolutions.
Flake depth
About cameras capture 8-flake video, which has similar limitations to 8-fleck JPEGs and can first to suspension up and show banding or posterization effects with heavy editing (or 'grading', to use the video term). Some cameras can capture 10-scrap video, which offers more scope for editing later.
Bitrate
Bitrate indicates the maximum data capture speed of a video camera and are related to the video resolution and quality settings. The higher the photographic camera's bitrate, the better the quality information technology can capture, broadly. 100Mbps (megabits per second) is good, simply high-end video cameras might offer 500Mbps. Bitrates don't tell you everything you lot need to know about a video camera's quality, but they exercise give you an idea of its professional person status and its recording 'horsepower'.

Cinematics lenses
Regular lenses are fine for video just cine lenses take special adaptations that can make video easier or better. They use T-stops (actual light transmission values) rather than F-stops, and many take 'de-clicked' aperture/iris rings for polish and silent exposure adjustment. Some also have toothed rings that appoint with professional pull-focus mechanisms.
Color subsampling
Video footage is very data-heavy and is recorded using a variety of pinch techniques. One of these is chroma (or color) subsampling, where the two blush channels of the video signal are compressed compared to the luma channel (the first of the three numbers). The technical explanations are complex, simply in that location are ii figures in common use right now. iv:ii:0 sampling gives good quality and expert compression and is the standard setting for most cameras capturing video to an internal retentiveness card. 4:two:ii sampling gives amend quality but needs either an external recorder or 1 of the latest, more advanced video cameras – some of these can capture four:2:2 video internally.
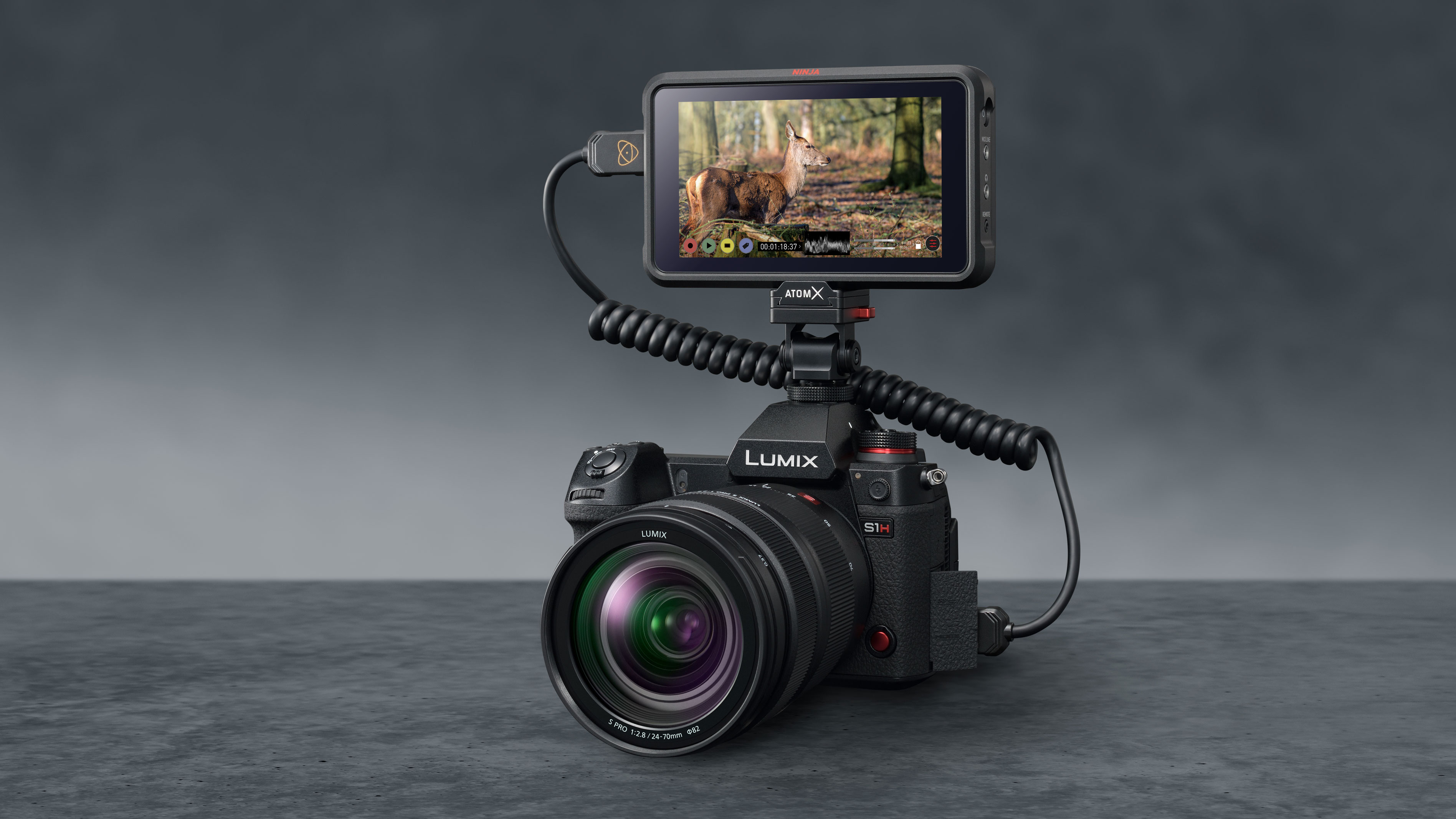
External recorders
Video cameras can record compressed video internally to memory cards, but you tin can usually tape 'make clean' (ie uncompressed) video to an external recorder via the camera'southward HDMI port, too. This offers potentially higher quality and greater storage capacity, and many of these have big displays that let you run into the scene more clearly. Some of the best on-photographic camera monitors have built-in video recorders.
Intra-frame vs inter-frame (IPB)
Intra-frame compression compresses each frame individually and gives the best quality frame by frame. Inter-frame compression only stores the changes betwixt key frames. The choice may exist expressed every bit 'All-I' (intra-frame) and 'IPB' (inter frame) compression.
Microphones
The camera'south internal microphone, stereo or otherwise, will not have the sound quality or directional sensitivity for adept-quality video, and then an external mic is an essential accompaniment. You can use directional 'shotgun' mics like this RODE VideoMic Pro, or a wireless lapel or 'lavalier' mic for clipping to article of clothing to tape speech. See our guide to the all-time microphones.
LED lighting (continuous lighting)
Naturally, wink is no good for video, so if yous intend using artificial light information technology will need to be continuous lighting. LED panels are the acme option for video considering they run for a long time off battery power while providing adept levels of lighting and low estrus levels. Some also offer variable color temperature for matching the color of different light sources. Come across our guide to the best LED panels.
Alive view
Mirrorless cameras accept an advantage because they offer full-time live view both on the rear screen and in the viewfinder. DSLRs only offer rear screen viewing because they have to shoot video with the mirror up.
Memory cards
memory card makers will quote a maximum transfer speed, which is useful for gauging their performance for stills photography, but for video you demand a minimum sustained speed. This is not the aforementioned thing, so the all-time memory cards now quote both. The bare minimum for 4K video is 10MB/s (Class 10, UHS Class one, V10); 30MB/due south is better (UHS Class three, V30) and 60MB/s is ideal (V60). Learn how to sympathise everything written on your camera'due south memory menu.
Tilting screen
Very useful when filming at low angles or footing level. Fully-articulating screens are less important for video considering you never shoot with the camera held vertically.
Touchscreen control
Useful in videography because y'all're less probable to jog the camera if y'all need to make adjustments while filming. Also invaluable when vlogging or content creating, giving you quick access to settings without having to navigate dials and buttons.
Video tripod and head
A dedicated video tripod, such as the Manfrotto tripod above, volition have twin legs for actress stability and vibration reduction, and a fluid head with a long panning arm will provide much smoother photographic camera movements. The Manfrotto Nitrotech N8 has both these features, together with a counterbalance system that prevents the photographic camera drooping forwards when it's released. See our guide to the best video tripods.
Zebras
A tool provided by many contempo cameras that'due south used to help approximate exposure. This displays the areas of highlights in the frame, and the user volition typically have control over the threshold to better manage detail in these areas.
8-scrap vs x-bit
Video footage is ordinarily captured using 8-fleck color – the same fleck-depth used for JPEG all the same images. This is commonly fine, unless the video needs heavy editing ('grading') later. Heavy editing can crusade the tones to start to pause up or posterise, losing their shine gradations. Some cameras tin can capture 10-bit video, either internally or when connected to an external recorder. This produces video which tin withstand editing much improve, which is especially important if y'all use Log modes (beneath).
All-I vs Long GOP
In gild to keep video file sizes manageable, further compression is used inside each frame or even between frames. All-I (all-intra) uses intra-frame pinch lonely, so that although each frame is compressed, each frame is nevertheless a complete image. Long GoP (long Group of Pictures) compression identifies significant keyframes (full frames) with big differences, and 'delta' frames in betwixt where there are only small differences – and records only these differences, non the full frame. Long GoP compression produces smaller video files, merely All-I compression produces better quality, especially for editing.

Raw video
Raw video is like raw images in stills photography. The camera records video as raw, unprocessed data rather than as processed, viewable flick files. However, raw video capture places MUCH bigger demands on processing ability and storage capacity, particularly at loftier resolutions similar 4K and above, so simply very loftier stop video cameras can capture raw footage internally, and fifty-fifty quite advanced models may demand an external recorder.
Log modes
Log modes are a kind of one-half way house towards the flexibility of raw video. They capture video which is tonally very flat only captures an extra-high brightness range to work with later when editing, or 'grading' the video. Log modes are an important pro characteristic in more than advanced cameras and mostly increase the price – though sometimes makers add together Log modes via a firmware update. When you grade Log footage yous will need to apply a profile to 'correct' the tones and colors to a normal advent, or a LUT (lookup tabular array) to create a specific cinematic colour palette or 'look'.

Codecs vs formats
This tin can be confusing considering it frequently sounds as if people are treating them as the same matter, merely they are not. Essentially, the video 'format' is the 'container' for the video, audio and assorted metadata to tie it all in together, while the 'codec' is purely the video pinch organization used. For example, the Sony A7S 3 uses an XAVC HS format which uses the H.265 video codec. The XAVC HS format is proprietary to Sony, only other makers apply the same H.265 video codec for their own video formats. The common MPEG-four format (also known as MP4 after its .mp4 file extension) uses the as mutual H.264 video codec. You need containers (formats) for video because they likewise take to store audio files and metadata needed by the maker to offer proprietary video features for playback and editing.
Read more:
• How to choose a video photographic camera
• Best cameras for vlogging
• All-time 4K cameras for filmmaking
• Best cinema cameras
• Microphone jargon explained
Related manufactures
Source: https://www.digitalcameraworld.com/features/video-jargon-explained-what-the-specs-mean-and-what-to-look-for
Posted by: waltersrehe1947.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Does P Mean On A Camera"
Post a Comment